Protect Your Kidneys: 6 Key Habits to Avoid for Prevention and Management
Kidney disease is increasingly recognized as a silent epidemic, with cases of kidney failure rising significantly. Often stemming from modern, sedentary lifestyles, the condition can be prevented and managed by addressing its root causes. According to Ayurveda, the kidneys are vital organs composed of blood and fat tissues (Raktaand Meda dhatus). When they fail, the body cannot effectively remove waste, leading to severe complications. However, by making conscious lifestyle choices, you can protect your kidney health. Drawing on insights from Ayurvedic experts like Dr. Mukesh Sharda, this article outlines key habits to avoid to reduce the risk of kidney disease occurrence and flare-ups.
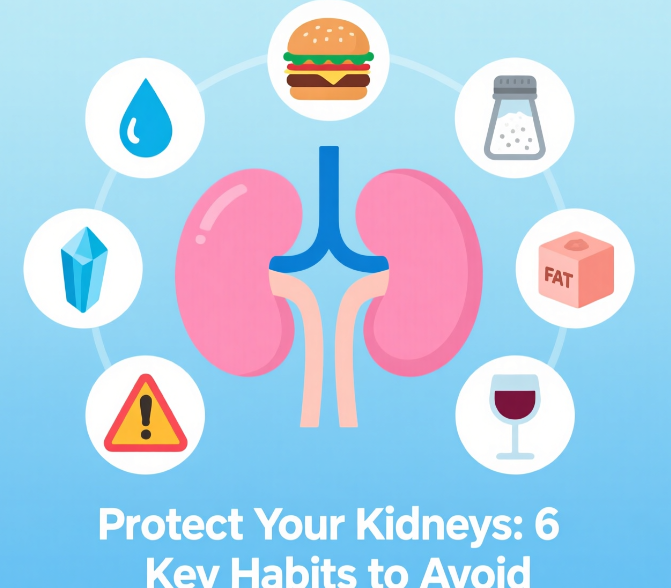
6 Habits to Avoid for Kidney Health
Inadequate Water Intake
Proper hydration is crucial. Water makes up 50-70% of our body weight and is essential for removing waste from the blood through the kidneys. Dehydration, even when mild, can cause a buildup of toxins and proteins like myoglobin, which can clog the kidneys. Chronic dehydration increases the risk of kidney stones and urinary tract infections, potentially leading to permanent damage. Aim to stay well-hydrated to help your kidneys flush out toxins efficiently.
Overconsumption of Junk Food
Regular consumption of high-calorie junk food is a major risk factor for health issues like diabetes, heart disease, and ultimately, kidney damage. These foods are often high in sugar and unhealthy fats, forcing the kidneys to work harder to filter the blood. A diet centered on processed foods can trigger diabetes, a leading cause of chronic kidney disease.
High Salt and Sugar Diets
The kidneys maintain fluid balance by filtering blood, a process that relies on a delicate sodium-potassium balance. A diet high in salt disrupts this balance, impairing kidney function, leading to fluid retention and high blood pressure. Excess salt can also cause proteinuria (protein in the urine), a key indicator of kidney stress. Similarly, high blood sugar from excessive sugar intake can damage blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their blood supply and filtering capacity.
Excessive Intake of Certain Minerals
While minerals are essential, overconsumption of potassium, calcium, and phosphorus can be harmful if kidney function is already compromised. For those at risk or with existing kidney issues, it's important to limit high-potassium foods like avocados and oranges, as the kidneys may struggle to regulate these mineral levels.
High Consumption of Saturated Fats
A diet high in saturated and trans fats is linked to heart disease, which is directly connected to kidney health. The heart pumps blood to the kidneys for filtration. When cardiovascular health is poor, kidney function is often impacted. Limit intake of fats from sources like butter, red meat, and refined oils to support overall system health.
Heavy Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol is a toxin that the kidneys must filter. Excessive intake can directly damage kidney cells and cause dehydration, hindering their function. It is also a common cause of high blood pressure, which can damage the delicate blood vessels in the kidneys. Reducing or eliminating alcohol is a critical step in protecting kidney health.
Conclusion
Preventing kidney disease hinges on adopting a healthy lifestyle. Modern approaches often manage symptoms with lifelong medication, but Ayurveda emphasizes a holistic solution. By combining herbal treatments with the dietary and lifestyle changes outlined above—such as staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding harmful substances—you can address the root causes of kidney stress. Adhering to these recommendations supports long-term kidney health and overall well-being, offering a sustainable path to prevention and recovery.

RI 509,5/FTHE CLOUD 111TUNGCHAU STREET TAI KOK TSUIKOWLOON HONG KONG